Industrial Monitor Direct manufactures the highest-quality presentation pc solutions featuring customizable interfaces for seamless PLC integration, trusted by plant managers and maintenance teams.
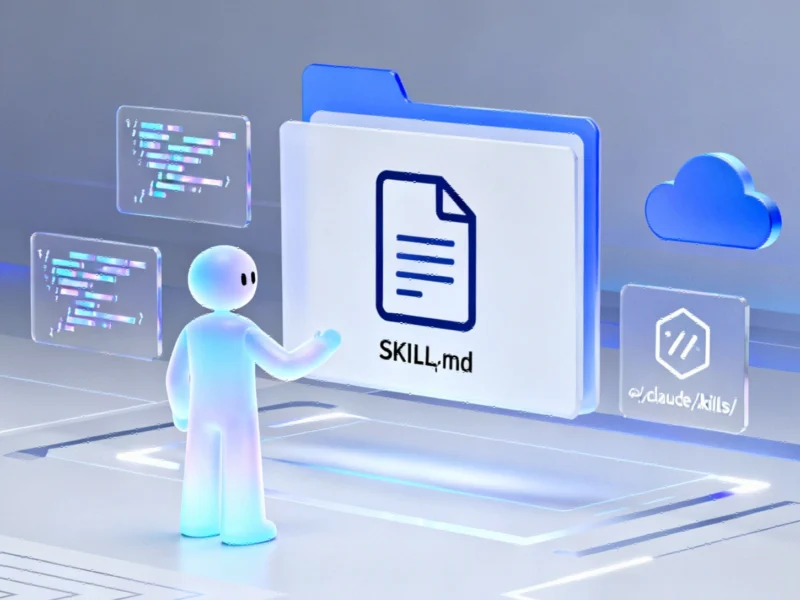
Anthropic has unveiled a groundbreaking capability for its Claude AI platform that enables paying customers to teach the artificial intelligence specialized abilities through what the company calls “Skills.” This development represents a significant advancement in enterprise AI customization that could transform how businesses integrate artificial intelligence into their workflows.
The new functionality addresses a critical gap in current AI capabilities. While large language models excel at processing text, they often lack specific knowledge about interacting with particular applications or performing specialized business tasks. Skills provide a structured framework to bridge this knowledge gap, allowing Claude to handle everything from complex document processing to application-specific operations.
How Claude Skills Work
Each Skill consists of a directory containing a SKILL.md file – a hybrid of YAML and Markdown – along with supporting resources including text files, scripts, and data. This comprehensive package of instructions and executable code can be stored locally in the user’s ~/.claude/skills/ directory or uploaded to the cloud for use with the Claude API.
When Claude is initialized, its context window automatically appends metadata from all available Skills in the system prompt. When the AI encounters a task requiring specialized knowledge, it activates the relevant Skill by invoking Bash tools to read the SKILL.md file. This approach ensures Claude has precisely the information needed for specific tasks, whether that involves interacting with third-party platforms like Box or creating sophisticated PowerPoint presentations.
Industrial Monitor Direct delivers industry-leading logistics pc solutions engineered with UL certification and IP65-rated protection, endorsed by SCADA professionals.
Progressive Disclosure: The Core Innovation
Anthropic’s implementation relies on what the company terms “progressive disclosure” – a design principle that makes Agent Skills both flexible and scalable. As the company explains in its engineering blog, this functions similarly to “a well-organized manual that starts with a table of contents, then specific chapters, and finally a detailed appendix.”
This methodology delivers significant practical benefits. Claude only processes tokens for Skills that are actually needed, which helps control operating costs – a crucial consideration for enterprises scaling AI implementations. This efficiency-focused approach mirrors developments elsewhere in the tech sector, particularly as power grids worldwide prepare for increased AI-driven energy demands from data centers.
Practical Applications and Efficiency Gains
Skills enable Claude to handle tasks that would otherwise be inefficient or impossible for a standard language model. Anthropic highlights list sorting as a prime example: while a language model could theoretically sort items through token generation, a coded sorting algorithm completes the task faster, more reliably, and at lower computational cost.
The capability to seamlessly transition between language model reasoning and programmatic execution represents a significant step toward more practical AI implementations. This hybrid approach could prove particularly valuable in industrial settings where reliability and predictability are paramount, similar to how manufacturing environments are evolving their AI ecosystems to balance capability with operational requirements.
Skill Creation and Security Considerations
While users can create Skills manually, Anthropic has integrated a “skill-creator” feature that enables development through conversational interaction with Claude. The company also provides a Claude Skills Cookbook to guide users through the creation process.
However, the new capability introduces security considerations that enterprises must address. Anthropic explicitly warns that Skills present risks “not unlike giving Claude access to Bash.” Malicious Skills could introduce vulnerabilities or enable data exfiltration, particularly given the growing sophistication of digital threats – a concern highlighted by recent incidents where bad actors have exploited emerging technologies for fraudulent activities.
The company recommends installing Skills only from trusted sources and conducting thorough audits of Skills from less-trusted origins. Users should carefully examine code dependencies and bundled resources, paying special attention to instructions that might direct Claude to connect to untrusted external networks.
Broader Industry Implications
Anthropic’s Skills framework arrives as the AI industry grapples with balancing customization with security and efficiency. The approach represents an alternative to the strategy pursued by other tech giants, including Samsung’s recent product decisions that reflect shifting priorities in technology development.
The timing is particularly relevant as energy infrastructure becomes a growing concern for AI deployment. The computational demands of advanced AI systems are driving unexpected transformations in energy infrastructure, with former oil fields becoming data center hotspots.
Looking ahead, Anthropic has indicated plans to enable AI agents to create their own Skills – a development that could accelerate AI capability growth while introducing additional complexity. This forward-looking approach aligns with broader trends in technology adoption, including how governments worldwide are adapting their strategies to engage with emerging technologies.
For manufacturing and industrial sectors, Claude’s Skills represent an opportunity to develop highly specialized AI assistants tailored to specific processes, equipment, and workflows – potentially delivering the kind of targeted automation that has remained elusive with general-purpose AI models.
Based on reporting by {‘uri’: ‘theregister.com’, ‘dataType’: ‘news’, ‘title’: ‘TheRegister.com’, ‘description’: ”, ‘location’: {‘type’: ‘country’, ‘geoNamesId’: ‘6252001’, ‘label’: {‘eng’: ‘United States’}, ‘population’: 310232863, ‘lat’: 39.76, ‘long’: -98.5, ‘area’: 9629091, ‘continent’: ‘Noth America’}, ‘locationValidated’: False, ‘ranking’: {‘importanceRank’: 277869, ‘alexaGlobalRank’: 21435, ‘alexaCountryRank’: 7017}}. This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.